Google AI Overviews Stats: How Things Stand In 2025
Google’s AI Overviews have become a central part of search results—but how often do they appear, how accurate are they, and what kind of impact are they having on businesses and users?
Here’s a detailed breakdown of everything you need to know, with the latest statistics and findings from industry studies.
Google AI Overviews Stats & Figures
How Often Do Google AI Overviews Appear?
- 29.9% of Search Queries Now Feature an AI Overview
A December 2024 study of 10,000 keywords across seven industries found AI Overviews appear in nearly one-third of search results. - Only 11.5% of Search Volume
Despite their presence in 29.9% of queries, AI Overviews account for just 11.5% of total search volume—suggesting they appear more in niche, mid-volume searches. - 42% of Mid-Volume Keywords Trigger AI Overviews
Queries with 501–2,400 monthly searches were the most likely to show AI Overviews.
Industry Breakdown: Where AI Overviews Appear Most
- 56% – Telecommunications
This industry had the highest rate of AI Overview appearances. - 14% – Beauty and Cosmetics
The lowest appearance rate was in this category.
Query Type Matters
- 74% – Problem-Solving Queries
These trigger AI Overviews more than any other category. - 69% – Question-Based Queries
AI Overviews are highly prevalent in queries that start with “how,” “why,” “what,” etc. - 33.3% – Non-Branded Searches
AI Overviews are far more likely to show up when you’re searching for general info rather than brand-specific content.
Timeline: How AI Overviews Rolled Out
- May 10, 2023: Google debuts SGE (Search Generative Experience) at I/O.
- May 25, 2023: Early access begins via waitlist.
- March 22, 2024: Testing expands to main search results.
- May 14, 2024: SGE officially becomes “AI Overviews.”
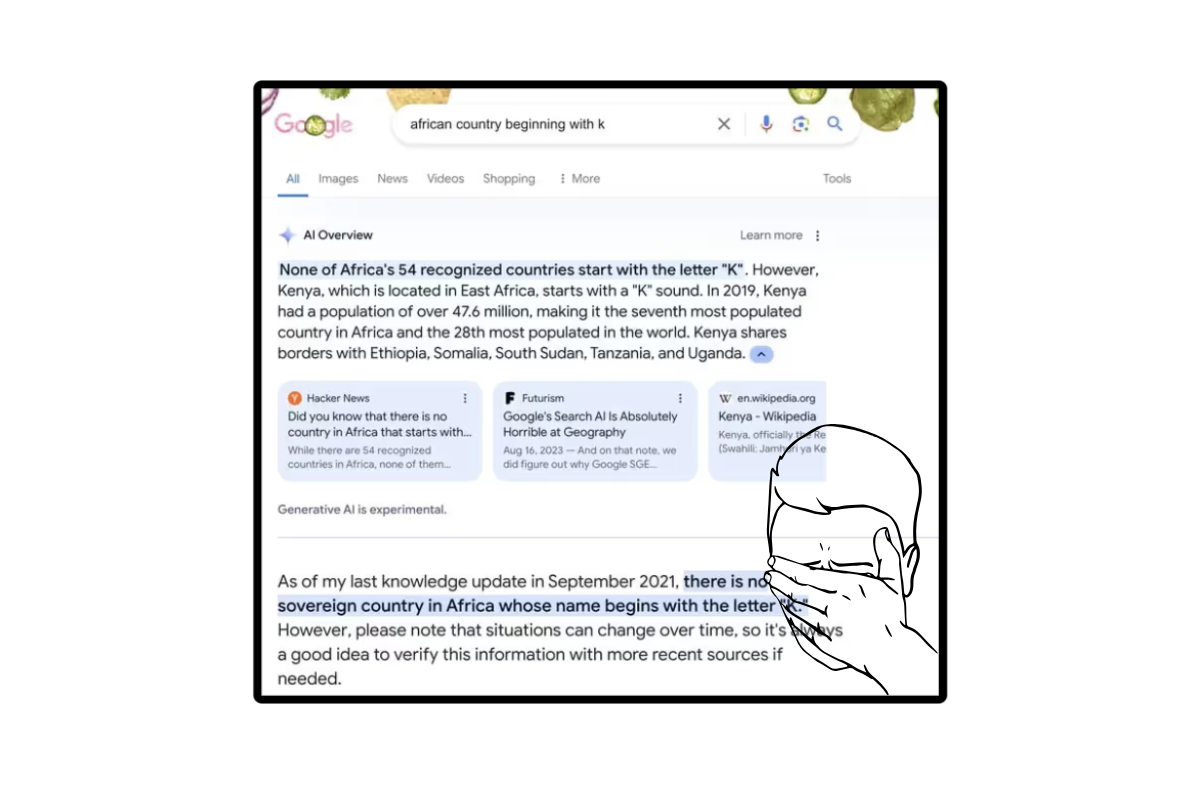
Accuracy Problems and AI Misinformation

Despite Google’s ambitions to enhance search with AI-powered summaries, AI Overviews have come under fire for repeatedly surfacing inaccurate, misleading, or outright bizarre information.
These issues have sparked growing concern among users, publishers, and industry experts about the reliability of AI-generated content in such a high-stakes context.
While Google claims AI Overviews improve the quality of search results, several high-profile mistakes have painted a different picture — one where the technology appears far from ready for prime time.
Documented Cases of Google AI Overviews FAILS
A growing list of examples highlights the inconsistencies and potential dangers of relying on AI Overviews for factual information:
- Dangerous Health Recommendations: One AI Overview suggested that taking a bath with a toaster had health benefits — a clear and dangerous safety risk.
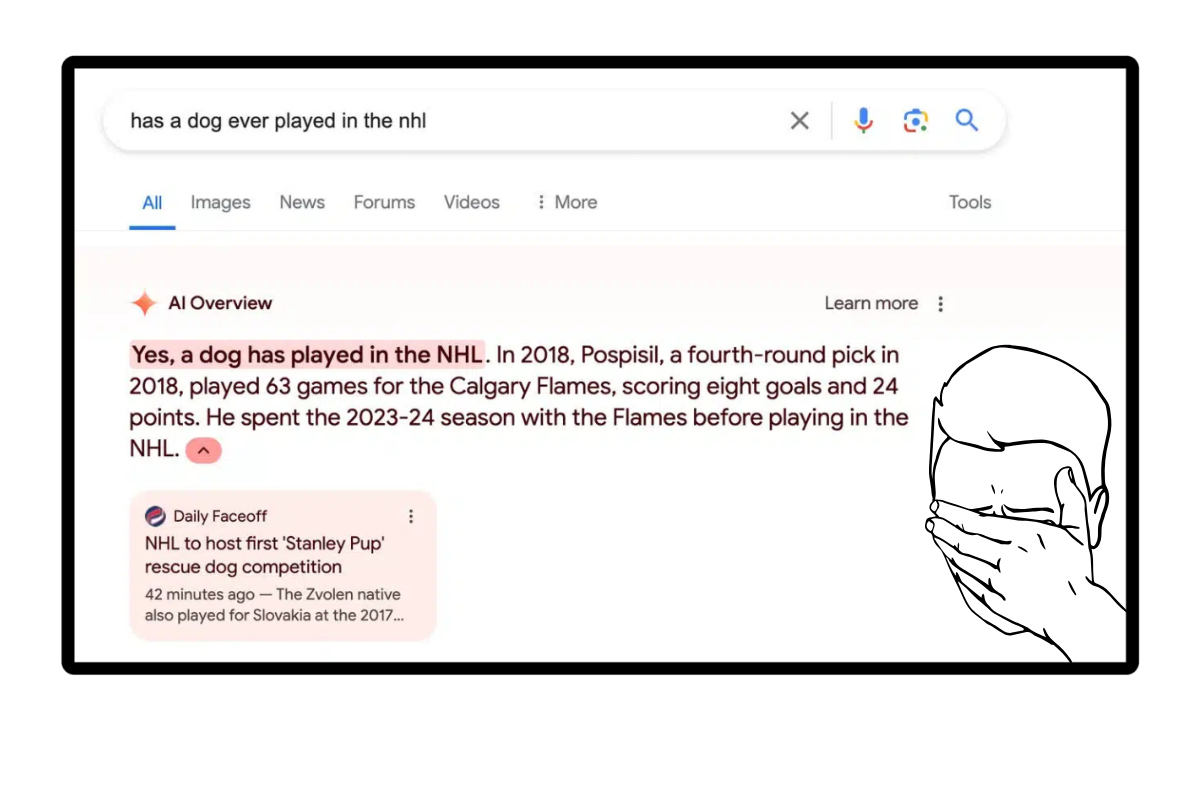
- Fictional Claims Treated as Fact: Another snippet bizarrely claimed that a dog had played in the NHL, presenting this absurd statement as legitimate information.
- Misinformation About Public Figures: In one instance, an AI Overview incorrectly stated Barack Obama’s religion, showing how AI systems can amplify longstanding misinformation without context or verification.
- Misinterpreted Satire: AI Overviews have also pulled from clearly satirical sources. One response cited The Onion, recommending that people eat rocks daily, mistaking the satirical article for a legitimate health tip.
- Low-Quality Forum Content Used as Source Material: Another example saw AI recommending non-toxic glue to make pizza sauce “stickier”, traced back to an old Reddit comment from a child — hardly a credible culinary source.
Why These Errors Matter
These aren’t just amusing anomalies — they raise serious questions about how Google’s AI evaluates content, determines authority, and filters sources.
When millions of users rely on Google Search for everything from health advice to homework help, even a small number of inaccurate or unsafe answers can have outsized consequences.
The problem seems rooted in the AI’s inability to distinguish authoritative sources from satire, outdated content, or low-quality user-generated material.
And because these summaries are presented at the top of the search results — often before organic links — many users may take them at face value without verifying the information.
Where’s the Bad Info Coming From?
- Satirical Sources: Example: Eating rocks daily sourced from The Onion.
- Unverified Comments: Advice about glue in pizza sauce traced to an 11-year-old Reddit comment.
Legal Backlash: The Chegg Lawsuit
- February 2025: Chegg files an antitrust lawsuit against Google.
- Claims that AI Overviews are cannibalizing their search traffic and pulling information without fair attribution.
- The lawsuit says this creates a “hollowed-out information ecosystem.”
Google’s Response:
Google argues that AI Overviews increase site diversity in search traffic and help distribute clicks more broadly.
New Features and Experiments
- Highlight Button: Lets users highlight parts of AI Overviews to prompt deeper searches with citations.
- Card-Style Overview Blocks: Organizes answers visually for broader queries.
- Product Comparisons: Google is testing more detailed comparison tools inside AI Overviews.
Key Takeaways
- Google is continuously tweaking and testing the experience, but tensions between user convenience and content creator sustainability persist.
- AI Overviews appear in roughly 30% of queries, especially in mid-volume, non-branded, and problem-solving searches.
- Misinformation issues remain a serious concern, with many examples traced to unreliable sources.
- The Chegg lawsuit marks a turning point, with businesses pushing back on AI-driven content visibility.